/Vehicles/Axis/Germany/08-Halftracks/Zugkraftwagen/File/Zugkraftwagen-pg2.htm | Last Up-date: 27-10-2025
Zugkraftwagen (Prime Movers)
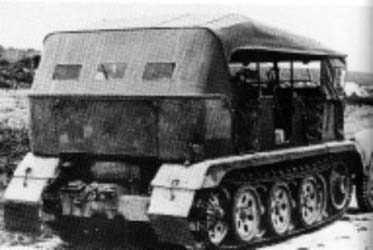
Sd.Kfz.6 mittlere Zugkraftwagen
5t Pioniere / Sd.Kfz.6/1 mittlere Zugkraftwagen 5t Artillerie /
Sd.Kfz.6/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit 3.7 cm Flak 36 /
Sd.Kfz.6/3 mit 76.2 mm Pak 36(r)/FK295(r) "Diana"
Le Sd.Kfz.6 fut produit de 1935 à 1943 par Büssing-NAG et Daimler-Benz. Quelques 1700 furent produits et utilisés comme transports de troupe ou comme tracteurs d'artillerie pour canons de 75 mm. Le Sd.Kfz.6 était plus lourd et plus coûteux que le Sd.Kfz.11 pour des performances non supérieures. Le Sd.Kfz.6 était réservé aux Pioniere et le Sd.Kfz.6/2 était un tracteur d'artillerie.
Sd.Kfz.6 was produced of 1935 to 1943 by Büssing-NAG and Daimler-Benz. Some 1700 were produced and used as transport of troop or as artillery tractors for guns of 75 mm. Sd.Kfz.6 was heavier and more expensive than Sd.Kfz.11 for nonhigher performances. Sd.Kfz.6 was reserved for Pioniere and Sd.Kfz.6/2 was an artillery tractor.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.6 mittlere Zugkraftwagen
5t Pioniere
|
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
 |
Sd.Kfz.6/1 mittlere Zugkraftwagen 5t Artillerie
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht
|
 |
Sd.Kfz.6/1 mittlere Zugkraftwagen 5t Artillerie
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht
|
Data |
Drawings |
| Sd.Kfz.6 BN15 (DB 15) |
| Sd.Kfz.6 (Late) |
| Sd.Kfz.6/1 |
Le Sd.Kfz.6/2 était un Sd.Kfz.6 équipé d'une superstructure spéciale accueillant le canon antiaérien de 37 mm Flak 36 à rotation complète. Le canon était équipé d'un bouclier et utilisés exclusivement dans un rôle antiaérien. Les munitions étaient transportées dans une remorque. La production débuta en 1941 et se termina en 1943 avec un total de 339 engins produits, qui seront versés dans les unités antiaériennes de la Lutwaffe. Plus tard le Sd.Kfz.6/2 fut remplacé par le Sd.Kfz.7/2.
Sd.Kfz.6/2 was Sd.Kfz.6 equipped with a special superstructure accomodating the anti-aircraft gun of 37 mm Flak 36 with complete traverse. The gun was equipped with a shield and used exclusively in an anti-aircraft role. The ammunition were transported in a trailer. The production began in 1941 and finished in 1943 with a total of 339 produced machines, which will be versed in the anti-aircraft units of Lutwaffe. Later Sd.Kfz.6/2 was replaced by Sd.Kfz.7/2.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.6/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit
3.7 cm Flak 36.
|
|
src: site Photos
Gallery of WW2 |
src: Site Panzer
Page von Reitsch |
Data |
Drawings |
| Sd.Kfz.6/2 Munitionsschlepper |
 |
Sd.Kfz.6/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit 5 cm Flak.
|
src: Connaissance de l'Histoire (Hachette),
n°5 - Août-Septembre 1978, Véhicules blindés
allemands 39-45
|
Drawings |
Le Sd.Kfz.6 équipé d'une superstructure arrière blindée, accueilli également le canon soviétique de 76.2 mm M1936 (76.2 mm FK 36(r) / FK 295(r) / Pak 36(r)). En 1941, 9 véhicules désignés 7.62 cm Pak 36(r) auf 5t ZkWg "Diana" furent réalisés. Entre janvier et février 1942, ils furent versés dans le 605e PzJg.Abteilung en Afrique du Nord.
Sd.Kfz.6 equipped with an armoured back superstructure, also accomodated the Soviet gun of 76.2 mm M1936 (76.2 mm FK 36(r) / FK 295(r)/Pak 36(r)). In 1941, 9 vehicles indicated 7.62 cm Pak 36(r) auf 5t ZkWg "Diana" were produced. Between January and February 1942, they were versed in the 605th PzJg.Abteilung in North Africa.
/Photo-01.lex.jpg) |
Sd.Kfz.6 mit 76.2 mm FK 36(r) / FK 295(r) /
Pak 36(r)
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht
|
76.2
mm Pal 36(r) L/56 Penetration of a shielding plate (mm) under a plunging angle of 30° |
|||||||
Ammo |
Weight |
Velocity |
100
m |
500 m |
1000
m |
1500 m |
2000
m |
| PzGr 39 | 7.6 kg |
720 m/s |
98 |
90 |
82 |
73 |
65 |
| PzGr 40 | 4.15 kg |
960 m/s |
135 |
116 |
94 |
75 |
58 |
Data |
Drawings |
Sd.Kfz.7 mittlere
Zugkraftwagen 8t / Sd.Kfz.7/1 Selbstfahrlafette mit 2 cm Flakvierling
/
Sd.Kfz.7/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit 3.7 cm Flak / Sd.Kfz.7/6 FlaKmesstruppkraftwagen
/
Feuerleitpanzerfahrzeug für V-2 Raketen auf Sd.Kfz.7
Très tôt, l'Allemagne réalisa très tôt l'importance des véhicules de soutien lors de ses avancés éclairs (Blitzkrieg) au début du conflit. Parmi la série de véhicules produits, le Sd.kfz 7 était un engin très réussi. Cet engin de 8 tonnes était principalement utilisé par les unités d'artillerie pour tracter le fameux canon antiaérien de 88 mm, mais aussi le canon lourd de campagne de 150 mm. Cet engin fut réalisé par la firme Krauss-Maffei et construit sur un châssis de camion conventionnel modifié. La suspension du train avant était constituée de ressorts à lames. Pour le train arrière (chenillé), les ressorts à lames et les barres de torsion étaient reliées à un train de roulement compact constitué de galets imbriqués (7 axes). Le Sd.Kfz.7 était propulsé par un moteur Maybach délivrant 140 chevaux et lui assurant une vitesse de pointe sur route d'environ 50 km/h. Polyvalent et fiable, le half-track de 8 tonnes fut considéré comme une réussite et fut l'un véhicules semi-chenillés le plus utilisé durant la guerre par l'armée allemande.
Very early, Germany very early realized the importance of the vehicles of support at the time of its fast advances (Blitzkrieg) in the beginning of the conflict. Among the series of produced vehicles, Sd.kfz 7 which was a very successful machine. This machine of 8 tons was mainly used by the units of artillery to tractor draw the famous anti-aircraft gun of 88 mm, but also the heavy field gun of 150 mm. This machine was realized by the firm Krauss-Maffei and built on a modified conventional truck chassis. The suspension of the nose gear consisted of leaf springs. For the rear (tracked) unit, the leaf springs and the torsion bars were connected to a train of compact bearing made up of overlapping road wheels (7 axes). Sd.Kfz.7 was propelled by a Maybach engine delivering 140 horses and ensuring to it a maximum speed on road from approximately 50 km/h. General-purpose and reliable, the half-tracked vehicle of 8 tons was regarded as a success and one of half-tracked vehicles was the most used during the war by the German army.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.7 mittlere Zugkraftwagen
8t
|
|
src: Militaria
Magazine "la campagne de Pologne", Histoire é&
Collections |
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.7 mittlere Zugkraftwagen 8t tractant
un Panzerjäger I sur une remorque en Afrique du Nord.
|
Sd.Kfz.7 mittlere Zugkraftwagen 8t trowing a
Panzerjäger I on a trailer in North Africa. |
src: Afrikakorps
in Action, squadron/signal publications |
src: Afrikakorps in Action,
squadron/signal publications |
Data |
Différentes versions furent réalisées incluant différents affûts mobile pour canons de DCA de 20 ou 37 mm En 1944, quand les V-2 furent utilisés de nombreux Sd.Kfz.7 furent convertis en postes de contrôle de tir. L'arrière du véhicule consistait en une superstructure accueillant l'équipement radio et de contrôle et protégeant l'équipage des flammes et des explosions. L'engin tractait également la plate-forme de tir du V-2 (Bodenplatte). Le Sd.Kfz.7/6 FlaKmesstruppkraftwagen était un tracteur d'artillerie doté d'équipements de télémétrie, destiné aux batteries d'artillerie.
Various versions were carried out including various mobile mountings for anti-aircraft guns of 20 or 37 mm In 1944, when V-2 were many used, Sd.Kfz.7 were converted into checkpoints of shooting. The back of the vehicle consisted of a superstructure accomodating the radio and control equipment and protecting the crew from the flames and the explosions. The machine also tractor drew the launching platform of V-2 (Bodenplatte). Sd.Kfz.7/6 FlaKmesstruppkraftwagen was a tractor of artillery equipped with distance measuring equipment, intended for the artillery batteries.
 |
 |
Feuerleitpanzerfahrzeug für
V-2 Raketen auf Sd.kfz.7.
|
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
Le Sd.Kfz.7/1 basé sur le Sd.Kfz.7 était équipé d'une superstructure spéciale accueillant le canon de 20 mm Flakvierling 38 à rotation complète. Les munitions étaient transportées dans une remorque. Le production débuta en 1943 et 319 exemplaires furent produits et versés dans les unités antiaériennes de la Lutwaffe.
Sd.Kfz.7/1 based on Sd.Kfz.7 was equipped with a special superstructure accomodating the gun of 20 mm Flakvierling 38 with complete traverse. The ammunition were transported in a trailer. The production began in 1943 and 319 specimens were produced and incorporated in the anti-aircraft units of Lutwaffe.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.7/1 Selbstfahrlafette mit
2 cm Flakvierling.
|
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
src: Normandie 44, Album Mémorial,
Ed.Heimdal |
20
mm Flakvierling 38 L/112.5 Penetration of a shielding plate (mm) under a plunging angle of 30° |
|||||||
Ammo |
Weight |
Velocity |
100
m |
500 m |
1000
m |
1500 m |
2000
m |
| PzGr | 0.148 kg |
780 m/s |
20 |
14 |
9 |
- |
- |
| PzGr 40 | 0.1 kg |
1050 m/s |
49 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
 |
Sd.Kfz.7/1 Selbstfahrlafette mit 2 cm Flakvierling.
|
src: Site Panzer
Page von Reitsch
|
Data |
Drawings |
| Sd.Kfz.7/1 mit 2cm Flakvierling |
Le Sd.Kfz.7/2 était un Sd.Kfz.7 équipé d'une superstructure spéciale pour l'installation du canon antiaérien de 37 mm Flak 36 à rotation complète. Les munitions étaient transportées dans une remorque. La production débuta en 1943 et 123 spécimens furent produits et versés dans les unités antiaériennes de la Lutwaffe.
Sd.Kfz.7/2 was Sd.Kfz.7 equipped with a special superstructure for the installation of the anti-aircraft gun of 37 mm Flak 36 with complete traverse. The ammunition were transported in a trailer. The production began in 1943 and 123 specimens were produced and incorporated in the anti-aircraft units of Lutwaffe.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.7/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit
3.7 cm Flak.
|
|
 |
Sd.Kfz.7/2 Selbstfahrlafette mit 3.7 cm Flak
w/armored cabin.
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht
|
Data |
Drawings |
| Sd.Kfz.7/2 mit 3.7cm Flak 43 |
Sd.Kfz.8 schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t / 88 mm Flak 18 Selbstfahrlafette auf Sd.Kfz.8
Le Sd.Kfz.8 fut produit de 1934 à 1944 en grande partie par Daimler-Benz, mais aussi dans une moindre mesure par Kraus-Maffei, Krupp ou Skoda. Environ 4000 furent produits et utilisés comme tracteurs d'artillerie. Un petit nombre furent équipés du 88 mm Flak 18. Le Sd.Kfz.8 sera encore fabriqué et utilisé après la guerre par l'armée tchécoslovaque.
Sd.Kfz.8 was produced from 1934 to 1944 mainly by Daimler-Benz, but also to a lesser extent by Kraus-Maffei, Krupp or Skoda. Approximately 4000 were produced and used as artillery tractors. A small number were equipped with the 88 mm Flak 18. Sd.Kfz.8 still manufactured and will be used after the war by the Czechoslovakian army.
 |
Sd.Kfz.8 schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht
|
Data |
En 1939, il fut demander par le Waffenamt d'équiper 10 Sd.Kfz.8 de canons antiaériens de 88 mm Flak 18. L'engin possédait une cabine blindée et une plate-forme accueillant le canon de 88 mm. Le canon avait une traverse limitée en position de tir horizontale à cause de la cabine, mais l'élévation du canon annulait ce problème. Ces engins furent utilisés comme véhicules antichars lourds et contre les positions fortifiées au sein du 8e Schwere Panzerjaegerabteilung en 1939 en Pologne et en France en 1940.
In 1939, it was to ask by Waffenamt to equip 10 Sd.Kfz.8 with anti-aircraft guns of 88 mm Flak 18. The machine had an armoured cabin and a platform accomodating the gun of 88 mm. The gun had a cross-piece limited in horizontal position of shooting because of the cabin, but the elevation of the gun cancelled this problem. These machines were used as heavy anti-tank vehicles and against the fortified positions within 8th Schwere Panzerjaegerabteilung in 1939 in Poland and France in 1940.
 |
 |
Sd.Kfz.8 schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t
mit 88 mm Flak.
|
|
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
src: Site Lexikon
der Wehrmacht |
88
mm Flak 18 L/56 Penetration of a shielding plate (mm) under a plunging angle of 30° |
|||||||
Ammo |
Weight |
Velocity |
100
m |
500 m |
1000
m |
1500 m |
2000
m |
| PzGr 39-1 | 10.2 kg |
1000 m/s |
203 |
185 |
165 |
148 |
132 |
PzGr 40-43 |
7.3 kg |
1130 m/s |
237 |
217 |
193 |
171 |
153 |
Sources:
- Connaissance de l'Histoire (Hachette) - N°5 - " Véhicules blindés allemands 39-45"
- Site "Achtung Panzer" - http://www.achtungpanzer.com
- Site "WWII Vehicles" - http://www.wwiivehicles.com
- Site "Second World War Armour" - http://www.onwar.com/tanks/index.htm



